Sleep Study Phillip
Sleep Study Phillip
How Sleep Diagnosis Improves Quality of Life and Long-Term…
Sleep affects nearly every part of daily life, from energy levels and focus to emotional balance and physical health. When sleep problems become ongoing, they often do more than cause tiredness—they can quietly impact long-term wellbeing. Sleep diagnosis helps uncover the cause of disrupted sleep and plays a key role in improving both quality of life and future health outcomes.
What Is Sleep Diagnosis and Why It Is Important
Sleep diagnosis is a medical process used to identify conditions that interfere with healthy, restorative sleep. Rather than assuming poor sleep is due to stress or lifestyle alone, it looks deeper to determine whether a specific sleep disorder is present.
This process is important because untreated sleep disorders can contribute to serious health issues over time. Accurate diagnosis ensures that symptoms are properly understood and managed, helping people sleep better and protect their overall health.
Common Sleep Disorders and Their Symptoms
Many sleep disorders affect people across different ages and lifestyles. Insomnia is one of the most common, involving difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking too early. Sleep apnoea causes repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep and is often linked with loud snoring and daytime fatigue.
Other conditions include restless legs syndrome, which creates uncomfortable leg sensations at night, and circadian rhythm disorders that disrupt natural sleep timing. Narcolepsy, although less common, leads to excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep episodes.
How Sleep Disorders Are Identified
Identifying sleep disorders requires a combination of careful assessment and specialised testing.
Clinical Evaluation
The diagnostic process usually begins with a detailed consultation. Healthcare professionals review sleep habits, lifestyle factors, medical history, medications, and daytime symptoms. Sleep questionnaires or diaries may be used to identify patterns and triggers affecting sleep quality.
Sleep Studies
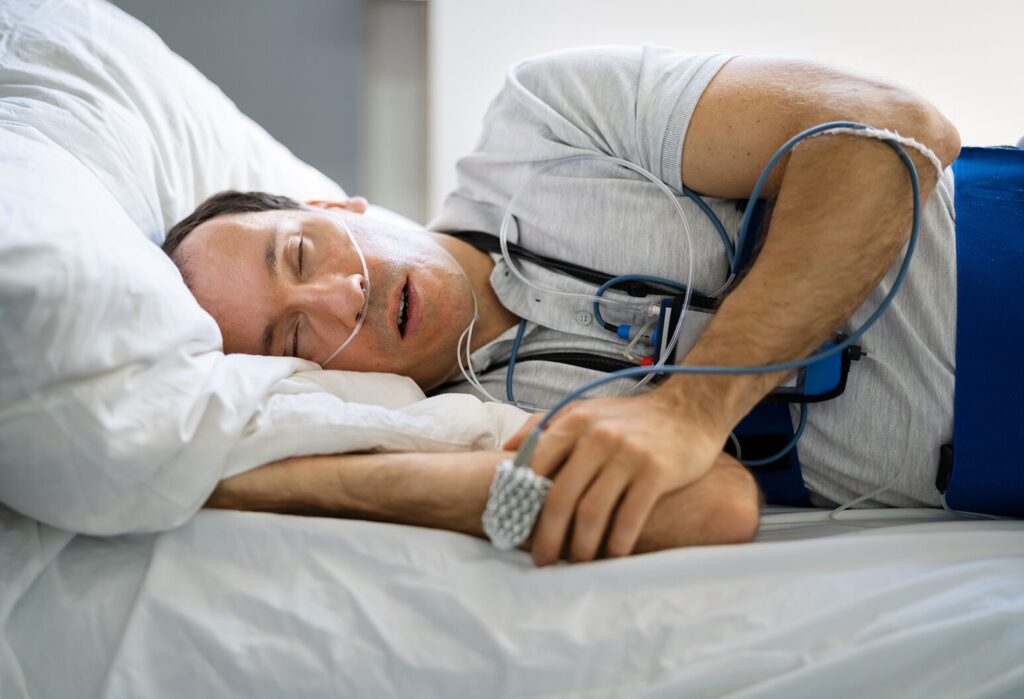
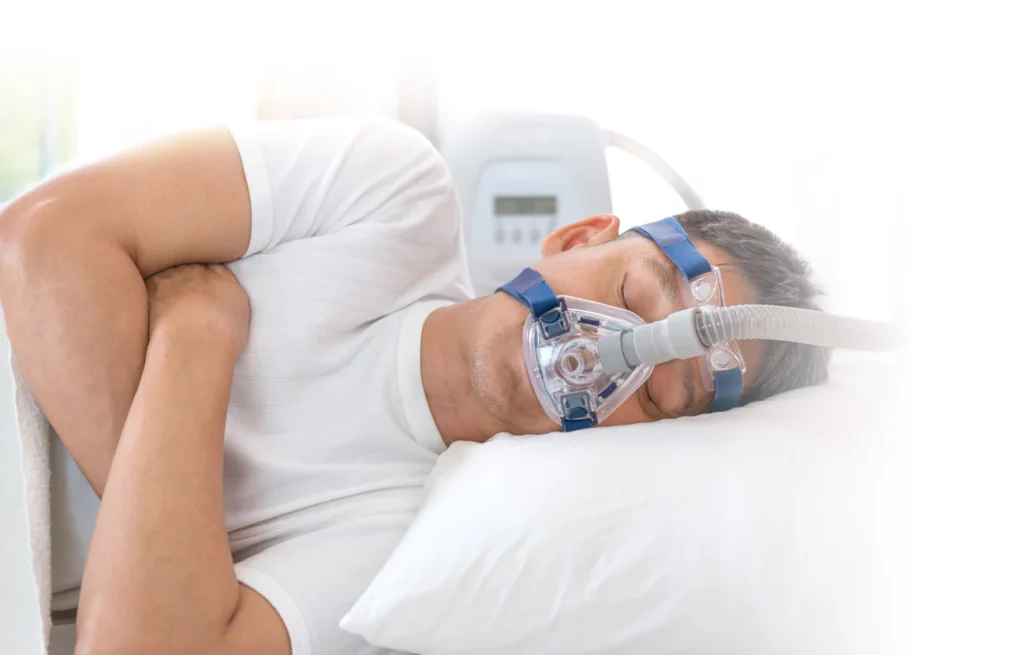
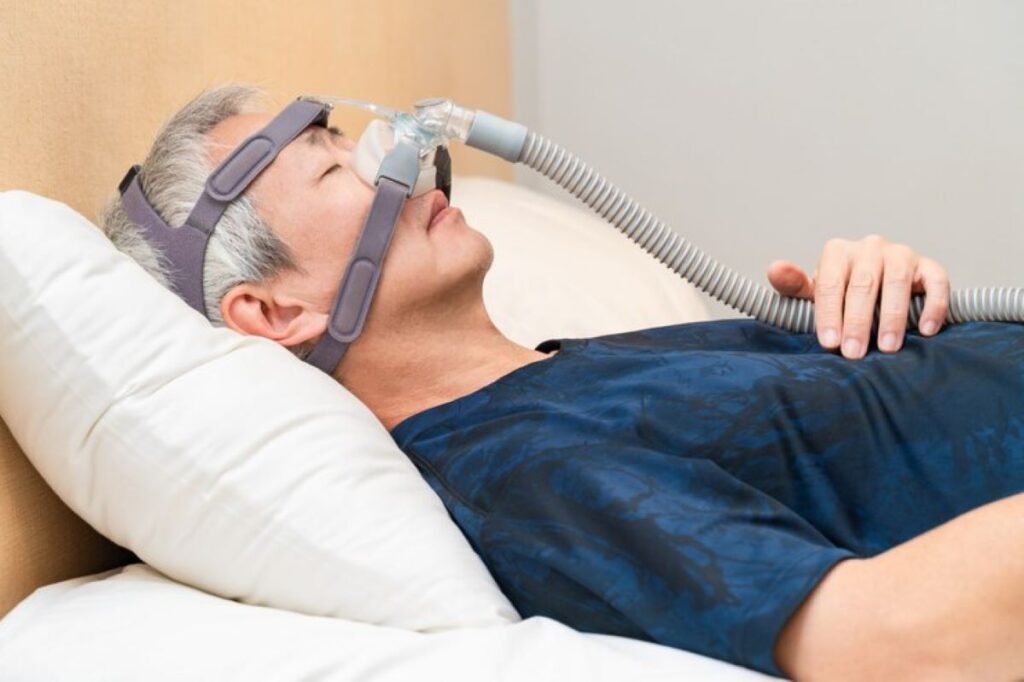
In-lab sleep studies, known as polysomnography, provide detailed information by monitoring breathing, brain activity, heart rate, oxygen levels, and movement during sleep. These studies are commonly used for diagnosing sleep apnoea and other complex sleep conditions.
Home Sleep Tests
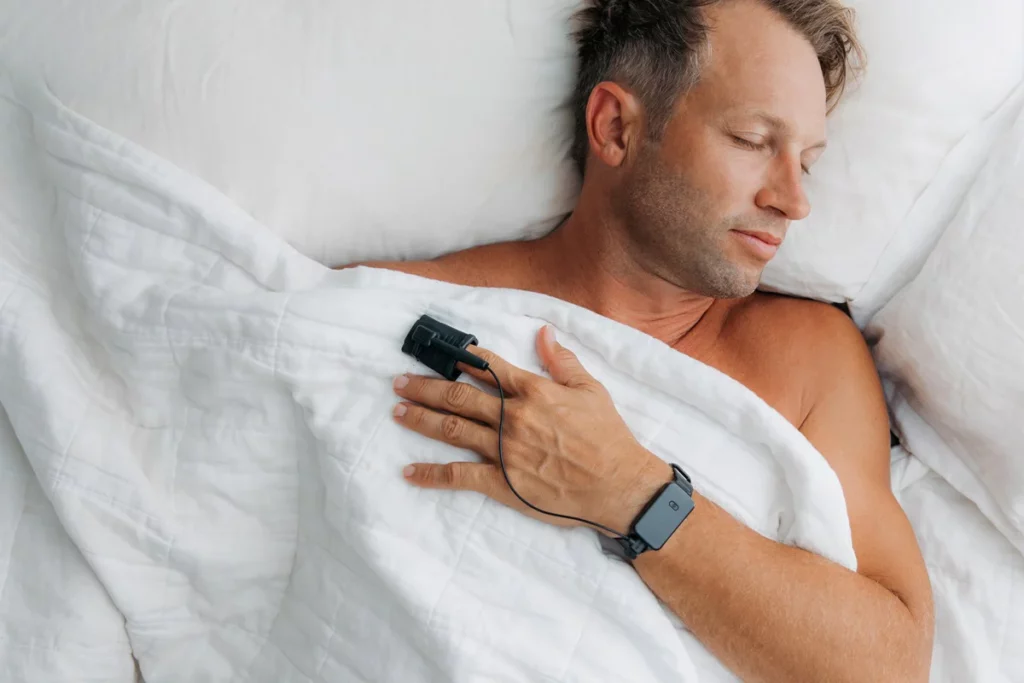
Home sleep testing may be recommended for certain individuals, especially when sleep apnoea is suspected. These tests allow people to sleep in their own environment while collecting essential data, offering a convenient alternative when appropriate.
Treatment Options After Diagnosis
Once a sleep disorder is diagnosed, treatment can be tailored to the individual’s needs. Behavioural therapies, such as cognitive behavioural therapy for insomnia, focus on improving sleep habits and addressing patterns that interfere with rest.
Medical treatments may include CPAP therapy for sleep apnoea, oral appliances, or medication when necessary. Lifestyle adjustments—such as maintaining consistent sleep routines, managing stress, and improving the sleep environment—often support long-term treatment success.
Benefits of Early and Accurate Sleep Diagnosis
Early and accurate sleep diagnosis can significantly improve daily life by restoring energy, improving concentration, and supporting emotional wellbeing. It also reduces the risk of long-term health problems such as heart disease, high blood pressure, mood disorders, and memory issues.
Accurate diagnosis prevents unnecessary trial-and-error treatments. When the true cause of sleep problems is identified early, individuals can follow a clear treatment plan that leads to lasting improvements in both sleep and health.
Conclusion
Sleep diagnosis is a powerful step toward better health and improved quality of life. By identifying the underlying causes of sleep problems, it allows for targeted treatment that restores healthy sleep patterns. Early and accurate diagnosis not only improves daily wellbeing but also supports long-term physical and mental health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does poor sleep affect long-term physical health?
Chronic sleep problems can increase the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and weakened immune function. Sleep diagnosis helps identify disorders that disrupt rest, allowing treatment to reduce ongoing strain on the body and support healthier long-term outcomes.
Can sleep diagnosis improve mood and emotional wellbeing?
Yes, diagnosing and treating sleep disorders often leads to noticeable improvements in mood, stress levels, and emotional balance. Better sleep supports brain function and emotional regulation, helping reduce irritability, anxiety, and low mood linked to ongoing sleep disruption.
Is sleep diagnosis useful even if I still function during the day?
Yes, many people continue daily activities despite poor sleep, but long-term effects may still occur. Sleep diagnosis helps identify hidden issues before they cause more serious health or performance problems, supporting early intervention and prevention.
Does treating sleep disorders improve memory and focus?
Improved sleep quality often leads to better concentration, memory, and mental clarity. Accurate diagnosis ensures the right treatment is applied, helping the brain recover and function more efficiently during the day.
Can sleep diagnosis help reduce reliance on sleep medications?
Yes, proper diagnosis can reduce unnecessary medication use. By addressing the underlying cause of sleep problems, treatment may focus on behavioural or medical solutions that improve sleep naturally, reducing the need for long-term sleep aid use.